Understanding the difference between than and then is crucial for effective communication in English. These two words, despite sounding similar, serve entirely different grammatical functions and can dramatically alter the meaning of a sentence when used incorrectly.
The English language is rich with linguistic complexities that challenge even native speakers. Word disambiguation becomes particularly important when dealing with homophones like than and then, which sound identical but carry distinct semantic meanings.
Etymology and Linguistic Origins
The words than and then have fascinating etymological backgrounds rooted in Germanic languages. Than emerges from Old English as a comparative word, while then developed as a temporal marker indicating sequence or time.
| Word | Old English Origin | Original Meaning | Modern Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Than | þanne | comparison marker | Comparative conjunction |
| Then | þanne | time indicator | Temporal adverb |
| Comparative | Comparative form | Distinguishing qualities | Highlighting differences |
| Temporal | Time-based reference | Sequential indicator | Showing time progression |
Grammatical Roles Unveiled
Comparative Analysis reveals distinct syntactic roles for these words. Than primarily functions as a comparison word, while then serves as a temporal sequence marker in sentences.
Than: The Comparison Champion
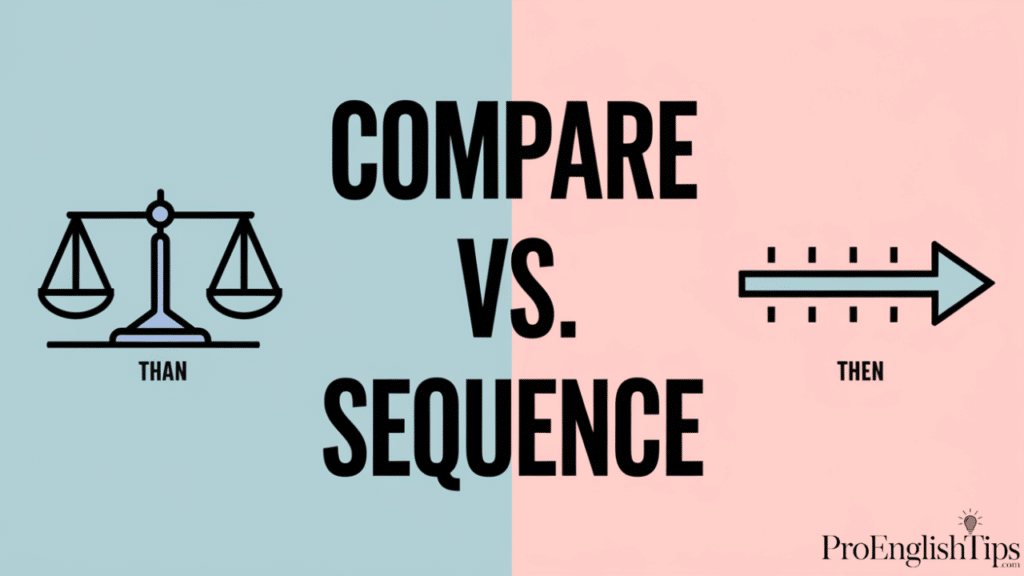
Than is predominantly used in comparative phrases to highlight differences or make comparisons. It connects two elements being evaluated against each other, revealing relative qualities or quantities.
Professional Email Example
Subject: Project Performance Comparison
Dear Michael,
Our team performed better than expected this quarter. We achieved more sales **than** last year's targets.
Best regards,
Sarah Thompson
In this email, than effectively compares performance metrics, demonstrating its comparative usage.
Then: The Time Traveler
Then operates as a temporal expression, indicating sequence, consequence, or time progression in sentences. It helps construct narrative flow and logical connections.
Academic Writing Scenario
Dear Professor Williams,
First, I completed the research draft. **Then**, I reviewed the methodology. Subsequently, I refined the analysis.
Sincerely,
Emily Rodriguez
Here, then illustrates a clear time sequence in the writing process.
Contextual Meaning and Semantic Usage
Linguistic usage demands precise understanding of word origins and contextual meaning. Professionals and students alike must master these subtle distinctions to communicate effectively.
| Scenario | Correct Usage | Incorrect Usage | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparing Quantities | More than 100 people | More then 100 people | Than indicates comparison |
| Sequence of Events | I studied, then took the exam | I studied, than took the exam | Then shows time progression |
| Expressing Preference | I prefer coffee than tea | I prefer coffee then tea | Comparative structure requires than |
Avoiding Common Grammatical Pitfalls
Word disambiguation becomes critical in preventing communication errors. Understanding the morphological analysis of these words helps writers choose correctly.
Professional writing demands language accuracy. Misusing than and then can undermine communication skills and perceived language proficiency.
You Might Like: Choosing or Chosing? Get It Right Every Time
Advanced Linguistic Insights
Sentence structure reveals intricate grammatical markers that distinguish these words. Conditional statements and cause-and-effect relationships often leverage these subtle linguistic tools.
| Linguistic Function | Than | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Part of Speech | Conjunction | Adverb |
| Primary Role | Comparison | Temporal Sequence |
| Common Contexts | Quantity, Quality Comparison | Time, Consequence |
| Example Phrase | Better than expected | Then we proceeded |
Writing with Precision
Developing writing clarity requires consistent practice in word choice. Language evolution continues to shape our understanding of these nuanced terms.
Professional Development Tips

Master the distinction between than and then by:
- Reading extensively
- Practicing written communication
- Seeking feedback
- Understanding grammatical conventions
The Path to Language Mastery
Language learning is a continuous journey of linguistic usage refinement. Embracing the subtle differences between than and then elevates one’s communication skills.
Final Thoughts on Linguistic Precision
Grammar rules are not restrictions but tools for clear expression. By understanding word differentiation, writers can communicate more effectively and professionally.
Key Differences Between “Than” and “Then”
Grammatical Foundations
The grammatical functions of “than” and “then” are fundamentally distinct, creating a crucial distinction in linguistic usage. Understanding these differences is essential for precise communication and language accuracy.
Than operates primarily as a comparative conjunction, while then serves as a temporal adverb. This fundamental difference dictates their unique roles in sentence construction.
| Grammatical Aspect | Than | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Comparison | Time Sequence |
| Typical Usage | Comparing quantities or qualities | Indicating order of events |
| Sentence Position | After comparative adjectives/adverbs | Can appear at various sentence positions |
| Typical Companions | More, less, better, worse | Next, after, subsequently |
Comparative Complexity of “Than”
When comparative analysis comes into play, “than” becomes the go-to word for highlighting differences. It introduces the second part of a comparison, revealing relationships between elements.
Example Professional Scenarios:
Comparative Email:
"Our new marketing strategy is more innovative than our previous approach."
Performance Review:
"Sarah performs better than most team members in complex problem-solving."
Temporal Nuances of “Then”
Then captures the essence of temporal sequence, marking the progression of time or logical consequence in a narrative.
Professional Communication Example:
Project Management Communication:
"We'll review the quarterly reports, then discuss strategic implementations."
Common Mistakes and Misuses
Frequent Grammatical Pitfalls
Word disambiguation becomes critical in preventing embarrassing communication errors. Writers often confuse these words due to their phonetic similarity.
| Common Mistake | Incorrect Sentence | Correct Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison Error | I like coffee then tea | I like coffee than tea | Than used for preferences |
| Temporal Confusion | He is than going home | He is then going home | Then indicates sequence |
| Comparative Blunder | More important then speed | More important than speed | Than for comparisons |
Context-Driven Misunderstandings
Semantic context plays a crucial role in distinguishing these words. Professional writers must develop keen linguistic awareness to avoid potential misinterpretations.
Professional Writing Scenario:
Incorrect: "Our team is stronger then our competitors."
Correct:"Our team is stronger than our competitors."
How to Remember the Difference
Mental Mapping Techniques
Developing language proficiency requires strategic memory techniques. Here are effective strategies for remembering the distinction between “than” and “then”.
| Memory Technique | Than Trigger | Then Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| Word Association | Compare = Than | Time = Then |
| Spelling Hint | Than has “a” like “comparison” | Then has “e” like “sequence” |
| Mental Image | Balancing scale for comparison | Clock or timeline for sequence |
Practical Learning Strategies
Language learning requires consistent practice and mindful observation. Develop your skills through:
Professional Practice Methods:
- Read extensively across various genres
- Practice writing comparative and sequential sentences
- Use grammar checking tools
- Seek feedback from colleagues or writing groups
Quick Reference Mental Trick
A simple mental trick:
- If you’re comparing something, use “than“
- If you’re talking about time or sequence, use “then“
Expert Communication Insight
Mastering these subtle linguistic nuances transforms good writing into exceptional communication. Language accuracy separates professional communicators from amateur writers.
Professional writers understand that grammatical precision is not about rigid rules, but about clear, effective expression.
You Might Like: Illicit vs Elicit: What is the Difference?
Advanced Linguistic Exploration
Syntactic Roles in Depth
Syntactic roles reveal the intricate grammatical functions of “than” and “then”. These words represent more than simple linguistic markers; they are fundamental to sentence structure and meaning communication.
| Syntactic Category | Than | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Part of Speech | Subordinating Conjunction | Adverb |
| Typical Sentence Position | Following Comparative | Can Start or Mid-Sentence |
| Grammatical Function | Comparative Introduction | Temporal/Sequential Marker |
| Semantic Role | Quantity/Quality Comparison | Time Progression/Consequence |
Etymological Journey
The word etymology of “than” and “then” traces back to Old English linguistic roots, demonstrating the linguistic evolution of these critical words.
Than originates from the Old English “þonne”, meaning “when” or “at that time”. Interestingly, its comparative function evolved gradually through linguistic development. Then similarly emerged from “þanne”, representing time and sequence.
Morphological Analysis
Morphological analysis provides deeper insights into the structural composition of these words. Their seemingly simple appearance masks complex linguistic usage patterns.
Professional Linguistic Breakdown:
- Than: Short, comparative conjunction
- Then: Temporal marker with flexible positioning
- Both words demonstrate Germanic language characteristics
Conditional and Complex Constructions
Beyond Simple Comparisons
Comparative phrases extend far beyond basic quantity comparisons. Advanced language users leverage “than” in nuanced conditional statements and complex expressions.
Example Complex Constructions:
Conditional Scenario:
"I would rather fail trying than succeed without effort."
Philosophical Expression:
"Nothing is more important than maintaining personal integrity."
Semantic Contextual Usage
Semantic context dramatically influences word selection. Professional communicators understand that context determines the precise meaning and appropriate word choice.
| Contextual Scenario | Than Usage | Then Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Comparative Analysis | Highlighting Differences | N/A |
| Time Progression | N/A | Marking Sequential Events |
| Cause-Effect Relationship | Limited Use | Indicating Consequential Flow |
Pragmatic Communication Strategies
Professional Writing Techniques
Writing clarity demands meticulous word selection. Understanding the subtle differences between “than” and “then” elevates communication skills.
Professional Writing Insights:
- Proofread for precise word usage
- Consider semantic implications
- Develop linguistic awareness
- Practice contextual application
Academic and Professional Contexts
Different writing environments require nuanced language proficiency. Academic, professional, and creative writing each demand distinct approaches to word selection.
| Writing Context | Than Importance | Then Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Writing | Precise Comparisons | Logical Sequence |
| Business Communication | Performance Benchmarking | Process Description |
| Creative Writing | Emotional Comparisons | Narrative Progression |
Psychological Aspects of Language Learning
Cognitive Processing of Homophones
Word disambiguation involves complex cognitive processes. The human brain must rapidly distinguish between similar-sounding words based on contextual cues.
Neurological Insights:
- Rapid context interpretation
- Semantic pattern recognition
- Instantaneous grammatical analysis
Language Acquisition Challenges
Language learning presents unique challenges in mastering subtle distinctions like “than” and “then”. Learners must develop linguistic intuition through consistent practice.
Technological Assistance
Digital Tools for Language Precision
Modern communication technologies offer sophisticated grammar rules enforcement and learning tools.
Digital Learning Strategies:
- Grammar checking software
- AI-powered writing assistants
- Online language learning platforms
- Interactive linguistic resources
Cultural and Global Perspectives
International English Variations
Language evolution manifests differently across global English-speaking communities. While core grammatical markers remain consistent, usage varies subtly.
| English Variant | Than Interpretation | Then Usage |
|---|---|---|
| American English | Straightforward Comparison | Clear Temporal Marker |
| British English | Nuanced Comparative Approach | Slightly More Formal Sequence |
| Australian English | Casual Comparative Style | Conversational Sequential Marker |
Pragmatic Language Applications
Nuanced Communication Strategies
Language proficiency extends far beyond simple grammatical correctness. The strategic use of “than” and “then” reveals sophisticated communication skills that distinguish exceptional communicators.
Professional Communication Insight: Mastering these words requires more than memorizing rules. It demands a deep understanding of contextual meaning and linguistic intuition.
Dialectical Variations
Linguistic usage varies across different English-speaking regions, introducing fascinating word differentiation nuances.
| English Dialect | Than Characteristics | Then Peculiarities |
|---|---|---|
| American English | Direct, straightforward comparisons | Clear sequential marker |
| British English | More formal comparative structures | Subtle temporal nuancing |
| Australian English | Casual, conversational approach | Relaxed sequential usage |
| Canadian English | Blend of British and American styles | Flexible temporal expression |
Computational Linguistics Perspective
Natural Language Processing Insights
Word disambiguation becomes a critical challenge in computational linguistics. Advanced language models must accurately interpret the subtle distinctions between “than” and “then”.
Computational Challenges:
- Context-based interpretation
- Semantic understanding
- Grammatical role recognition
Machine Learning Approaches
Syntactic roles and grammatical functions require sophisticated algorithms to distinguish between these seemingly simple words.
| Machine Learning Consideration | Than Analysis | Then Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Contextual Recognition | Comparative Pattern | Temporal Sequence |
| Semantic Interpretation | Quality/Quantity Comparison | Time Progression |
| Grammatical Role Detection | Conjunction | Adverbial Marker |
Psychological Linguistics
Cognitive Processing Mechanisms
The human brain performs remarkable feats of linguistic usage when distinguishing between “than” and “then”. Cognitive linguistics reveals fascinating insights into language processing.
Neurological Language Processing:
- Rapid contextual interpretation
- Instantaneous grammatical analysis
- Semantic pattern recognition
Language Acquisition Dynamics
Language learning involves complex cognitive mechanisms that go beyond simple memorization.
Developmental Language Stages:
- Initial rule-based learning
- Pattern recognition
- Contextual adaptation
- Intuitive application
Philosophical and Rhetorical Dimensions
Linguistic Philosophy
Words like “than” and “then” represent more than mere grammatical tools. They embody linguistic evolution and human communication’s profound complexity.
Philosophical Reflection: Language is a living, breathing entity that constantly adapts, with words like “than” and “then” serving as intricate markers of human thought and expression.
Rhetorical Sophistication
Comparative phrases and temporal expressions become powerful rhetorical devices in skilled communication.
Rhetorical Techniques:
- Comparative emphasis
- Temporal narrative construction
- Logical sequence establishment
Advanced Communication Strategies
Contextual Mastery
Semantic context transforms grammatical rules into art. Truly exceptional communicators understand the nuanced power of “than” and “then”.
Professional Communication Strategies:
- Develop contextual awareness
- Practice mindful word selection
- Embrace linguistic flexibility
Interdisciplinary Language Use
Different professional domains leverage “than” and “then” with unique sophistication.
| Professional Domain | Than Application | Then Utilization |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Writing | Precise comparisons | Methodological sequence |
| Legal Documentation | Comparative analysis | Chronological reporting |
| Technical Writing | Quantitative comparisons | Process description |
| Academic Research | Scholarly comparisons | Research methodology |
Emerging Language Trends
Digital Communication Impact
Modern communication platforms continuously shape linguistic usage, influencing how we understand and apply words like “than” and “then”.
Digital Language Evolution:
- Abbreviated communication
- Contextual compression
- Rapid linguistic adaptation
Future Linguistic Predictions
Language development suggests potential evolutionary paths for these fundamental words.
Potential Future Trends:
- Increased contextual flexibility
- More nuanced comparative structures
- Enhanced computational language processing
Conclusion: Beyond Grammatical Boundaries
Understanding “than” and “then” transcends mere grammatical correctness. It represents a journey into the profound depths of human communication, linguistic evolution, and cognitive complexity.
True language mastery emerges not from rigid rule-following, but from deep, intuitive understanding of linguistic subtleties.

Emma Carter is an experienced blogger at Pro English Tips. She loves helping people improve their English skills, especially through synonyms and creative language use. With a friendly writing style, Emma makes learning fun and easy for everyone. In her spare time, she enjoys reading and exploring new words, always looking for ways to inspire her readers on their journey to better communication.