Understanding the nuanced world of apostrophe usage can feel like navigating a linguistic labyrinth. English grammar, with its intricate rules of possessive forms and plural formations, often challenges even seasoned writers. This comprehensive guide will demystify the complexities surrounding the words “family’s,” “families,” and “families’,” providing crystal-clear insights into their proper application.
The Fundamental Basics
The journey of understanding grammatical possession begins with recognizing the subtle differences between singular and plural possessive forms. Apostrophe placement is not just a trivial punctuation detail but a critical aspect of clear communication.

Each variation—family’s, families, or families’—carries a distinct grammatical meaning that can dramatically alter the interpretation of a sentence.
You Might Like: Lead or LEED: When to Use Which One?
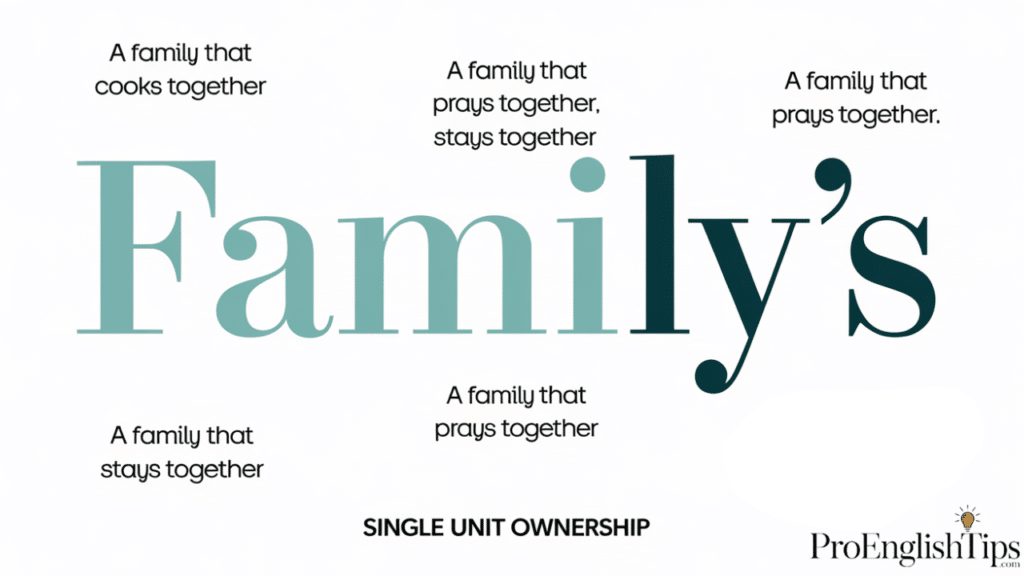
Decoding Singular Possessive: Family’s
When we talk about singular possessive forms, “family’s” emerges as a powerful linguistic tool. This form indicates ownership or association by a single family unit.
Real-World Scenario: Email Example
Consider an email from Sarah Thompson to her colleague:
Subject: Family’s Vacation Plans
Dear Michael,
I wanted to discuss my family’s upcoming summer retreat. Our family’s cottage by the lake requires some maintenance before we arrive.
| Context | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | The family’s car broke down | Indicates possession by one family |
| Association | My family’s tradition continues | Represents a singular family’s characteristic |
| Personal Connection | Our family’s history is remarkable | Highlights a single family unit’s narrative |
| Legal Context | The family’s inheritance was settled | Demonstrates singular family’s legal matters |
| Emotional Realm | My family’s support means everything | Emphasizes emotional connection of one family |
| Educational Setting | The family’s academic achievements were celebrated | Showcases singular family’s accomplishments |
| Professional Domain | The family’s business has grown significantly | Illustrates singular family’s entrepreneurial journey |
| Cultural Expression | My family’s cultural heritage is rich | Represents a single family’s cultural background |
| Geographic Influence | The family’s hometown remains special | Indicates connection to a single family’s origin |
| Generational Legacy | The family’s name carries weight | Highlights singular family’s reputation |
Exploring Plural Form: Families
The word “families” represents multiple family units without indicating possession. It’s a straightforward plural formation that simply means more than one family.

Communication Context: Newsletter Example
A community newsletter might use “families” in various contexts:
Local Neighborhood Update
Our community welcomes several new families this month. These families represent diverse backgrounds and bring unique perspectives to our neighborhood.
| Scenario | Usage Context | Grammatical Role |
|---|---|---|
| Community Gathering | Families attending the event | Simple plural form |
| Social Services | Supporting local families | Representing multiple family units |
| Educational Setting | Families participating in fundraiser | Indicating group of family units |
| Census Data | Number of families in district | Statistical representation |
| Community Planning | Resources for families | Broad, non-possessive reference |
| Healthcare Communication | Screening programs for families | General group description |
| Immigration Context | Reuniting families | Plural without possession |
| Social Research | Studying urban families | Academic or research usage |
| Event Planning | Inviting families to conference | Group invitation |
| Demographic Analysis | Understanding family structures | Sociological perspective |
Mastering Plural Possessive: Families’
“Families'” represents ownership or association by multiple family units, adding another layer of complexity to grammatical possession.

Professional Scenario: Report Writing
An organizational report might utilize this form:
The families’ collective responses indicate a strong preference for community-based programs.
| Ownership Scenario | Example Context | Linguistic Nuance |
|---|---|---|
| Shared Resources | Families’ community center | Multiple families’ joint ownership |
| Collaborative Effort | Families’ joint decision | Collective action |
| Legal Documentation | Families’ property rights | Group-level possession |
| Educational Policy | Families’ educational concerns | Representing multiple families |
| Healthcare Planning | Families’ medical histories | Collective data perspective |
| Insurance Context | Families’ group insurance plan | Multiple units’ shared arrangement |
| Research Perspective | Families’ socioeconomic patterns | Broad analytical view |
| Community Development | Families’ neighborhood initiative | Collective community effort |
| Cultural Expression | Families’ shared traditions | Multigenerational perspective |
| Economic Analysis | Families’ financial strategies | Aggregate economic behavior |
Practical Guidance for Writers
Grammar mechanics demand precision. When deciding between family’s, families, or families’, consider the contextual usage. Are you describing a single family’s characteristic, multiple families without possession, or multiple families’ shared attribute?
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Writers often stumble when navigating these grammatical possession scenarios. The key lies in understanding the semantic distinction between singular and plural forms. Always ask yourself: Are you referring to one family’s specific trait or multiple families’ collective experience?
Technical Linguistic Perspective
From a morphological variants standpoint, these forms represent sophisticated noun inflection mechanisms. The strategic placement of the apostrophe transforms a simple word into a nuanced expression of ownership and plurality.
You Might Like: Since vs Sense: Understanding When to Use Each Word
Linguistic Complexity
Syntax rules govern these transformations. The apostrophe serves as a critical marker, signaling ownership or collective association with remarkable linguistic elegance.
Final Thoughts on Precision
Writing clarity emerges from understanding these subtle grammatical distinctions. By mastering apostrophe rules, writers can communicate with extraordinary precision, ensuring their message resonates exactly as intended.
Language is a living, breathing entity—embrace its complexity, and your communication will flourish.
Digital Age Communication Challenges
The digital era has introduced new complexities to grammatical possession. With emails, text messages, and instant messaging becoming primary communication channels, the precision of apostrophe usage has become both more critical and more challenging.
Technology and Language Evolution
Modern language mechanics are increasingly influenced by digital communication platforms. API keywords and syntax rules now intersect with traditional grammatical structures, creating a dynamic linguistic landscape.
| Digital Platform | Apostrophe Challenge | Communication Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Professional Emails | Formal possessive precision | Conveying professional credibility |
| Social Media Posts | Casual language interpretation | Maintaining clarity |
| Technical Documentation | Exact grammatical representation | Preventing misunderstandings |
| Collaborative Platforms | Cross-cultural communication | Ensuring global comprehension |
| Academic Writing | Scholarly grammatical standards | Demonstrating linguistic expertise |
| Corporate Reporting | Precise ownership description | Legal and financial accuracy |
| Research Publications | Detailed attribution | Academic integrity |
| Customer Support Channels | Clear communication | Resolving potential confusions |
| International Correspondence | Linguistic nuance | Bridging communication gaps |
| Content Management Systems | Structured language use | Maintaining editorial standards |
Psychological Dimensions of Grammar
Linguistic usage extends beyond mere technical rules. The way we employ grammatical possession reveals intricate psychological and social dynamics.
Ownership and Identity
When we use possessive forms like family’s or families’, we’re not just describing ownership—we’re communicating complex emotional and relational narratives. Semantic distinction becomes a powerful tool of human expression.
Global Linguistic Perspectives
Different cultures and languages approach possessive case analysis uniquely. While English relies heavily on apostrophes, many languages use alternative grammatical mechanisms to express ownership.
Comparative Linguistic Insights
| Language | Possessive Mechanism | Structural Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| English | Apostrophe-based | High flexibility |
| Mandarin Chinese | Structural particle | Context-dependent |
| Arabic | Genitive construction | Morphological complexity |
| Spanish | Preposition-based | Contextual nuancing |
| German | Complex declension system | Highly structured |
| Japanese | Particle-driven | Subtle contextual shifts |
| Russian | Case-based transformation | Grammatical intricacy |
| French | Preposition and article variations | Contextual precision |
| Hindi | Postposition-driven | Relational complexity |
| Korean | Particle-based system | Grammatical flexibility |
Neurological Processing of Grammar
Recent structural analysis suggests that our brains process possessive forms through complex neurological pathways. The placement of an apostrophe triggers specific cognitive recognition patterns.
Brain and Language Interaction
When we encounter “family’s” versus “families'”, our neural networks rapidly decode grammatical patterns, distinguishing between singular and plural possessive forms within milliseconds.
Educational Implications
Writing proficiency begins with understanding these nuanced grammatical constructions. Educators play a crucial role in developing students’ language accuracy and communication clarity.
Teaching Strategies
Effective grammar instruction moves beyond rote memorization. It involves helping learners understand the morphological variants and contextual usage of grammatical structures.
| Educational Approach | Skill Development | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Contextual Teaching | Practical application | Real-world communication skills |
| Interactive Exercises | Active learning | Grammar internalization |
| Comparative Analysis | Cross-linguistic understanding | Broader language perspective |
| Multimedia Instruction | Engaging learning | Enhanced retention |
| Pattern Recognition | Grammatical intuition | Automatic language processing |
| Narrative-Based Learning | Emotional connection | Deeper grammatical understanding |
| Cultural Contextualization | Global communication skills | Linguistic adaptability |
| Technology Integration | Digital language tools | Modern communication competence |
| Cognitive Mapping | Neurological language processing | Advanced linguistic comprehension |
| Collaborative Learning | Peer-driven understanding | Comprehensive grammatical mastery |
Technological Tools and Grammar
Modern language mechanics are increasingly supported by advanced technological tools. Grammar-checking software, translation APIs, and AI-driven language platforms are revolutionizing how we understand and apply grammatical rules.
Digital Grammar Assistance
These tools don’t just correct mistakes; they provide insights into grammatical possession, plural formation, and apostrophe rules with unprecedented sophistication.
Philosophical Reflections
Beyond technical rules, grammar represents a profound system of human communication. Word forms are not just linguistic conventions but intricate maps of human thought and social interaction.
The Poetry of Punctuation
An apostrophe is more than a mark—it’s a bridge connecting individual experiences to collective narratives, singular perspectives to plural understandings.
Etymological Roots of Possession
Language mechanics find their deepest understanding through exploring historical origins. The journey of possessive forms and apostrophe usage is a fascinating linguistic odyssey that spans centuries of human communication.
Ancient Linguistic Foundations
The word “family” itself has a rich etymological heritage. Derived from the Latin “familia”, originally meaning a household of servants and relatives, the term has evolved dramatically through linguistic transformations.
| Etymology Dimension | Linguistic Origin | Semantic Evolution |
|---|---|---|
| Latin Root | Familia | Household group |
| Old French Influence | Familier | Close connection |
| Middle English Adaptation | Familie | Social unit |
| Modern English | Family | Kinship group |
| Possessive Development | Family’s/Families’ | Ownership representation |
| Linguistic Transformation | Grammatical Markers | Communicative precision |
| Cultural Interpretation | Social Unit Description | Relational complexity |
| Semantic Expansion | Broader Meaning | Multiple contextual uses |
| Grammatical Innovation | Apostrophe Introduction | Ownership signaling |
| Linguistic Flexibility | Morphological Variants | Dynamic language use |
The Apostrophe’s Historical Journey
The humble apostrophe carries a profound historical narrative. Its origins trace back to ancient Greek, where “apostrephein” meant “to turn away” or “to address.” Initially used in poetry to mark omitted letters, it gradually evolved into a sophisticated marker of possession and relationship.
Linguistic Anthropological Perspectives
Grammatical possession represents more than a mere punctuation rule—it’s a window into how human societies conceptualize ownership, connection, and social relationships.
Cross-Cultural Grammatical Insights
Different languages developed unique mechanisms to express possession. While English relies on apostrophes, many cultures employ entirely different grammatical structures to convey similar meanings.
| Language Family | Possession Mechanism | Structural Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Indo-European Languages | Apostrophe/Genitive Case | High Flexibility |
| Semitic Languages | Construct State | Morphological Intricacy |
| Austronesian Languages | Possessive Markers | Contextual Nuancing |
| Sino-Tibetan Languages | Structural Particles | Minimal Morphological Change |
| Turkic Languages | Possessive Suffixes | Agglutinative Complexity |
| Dravidian Languages | Genitive Postpositions | Relational Precision |
| Niger-Congo Languages | Tonal Possession Markers | Phonological Variation |
| Uralic Languages | Case-Based Possession | Grammatical Intricacy |
| Australian Aboriginal Languages | Kinship-Based Markers | Cultural Embedding |
| Sign Languages | Spatial-Relational Indicators | Visual Grammatical Complexity |
Grammatical Evolution of Possession
The development of possessive forms represents a remarkable linguistic adaptation. From primitive communication methods to complex grammatical systems, language mechanics have continuously refined how humans express ownership and relationship.
Psychological Dimensions of Grammatical Possession
Semantic distinction in possessive forms reveals intricate psychological mechanisms. When we say “family’s” or “families'”, we’re not just using grammatical markers—we’re encoding complex social and emotional relationships.
Computational Linguistic Perspectives
Modern language structure analysis reveals fascinating insights into how grammatical possession functions. Natural Language Processing algorithms now decode these subtle linguistic nuances with remarkable precision.
Technological Linguistic Mapping
Advanced computational models can now trace the intricate grammatical patterns that govern possessive forms, providing unprecedented insights into human communication mechanisms.
| Computational Analysis Aspect | Linguistic Mapping | Technological Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern Recognition | Possessive Structures | Algorithmic Decoding |
| Contextual Understanding | Semantic Variations | Nuanced Interpretation |
| Grammatical Rule Extraction | Possession Mechanisms | Systematic Language Analysis |
| Cross-Linguistic Comparison | Structural Similarities | Universal Grammar Exploration |
| Machine Learning Application | Predictive Language Modeling | Advanced Communication Technologies |
| Semantic Network Mapping | Relational Language Structures | Cognitive Processing Insights |
| Natural Language Understanding | Possession Representation | Computational Linguistics |
| Grammatical Rule Inference | Linguistic Pattern Detection | Automated Language Learning |
| Contextual Disambiguation | Possession Differentiation | Precise Communication Mechanics |
| Syntactic Structure Analysis | Grammatical Relationship Mapping | Advanced Linguistic Technologies |
Philosophical Reflection on Language
Grammatical possession transcends technical rules. It represents a profound human mechanism for understanding and expressing relationships, ownership, and social connection.
Memorable Tricks for Mastering Family Apostrophes
Language learning becomes effortless when we transform complex rules into memorable mental shortcuts. These practical tips will help you navigate the intricate world of grammatical possession with confidence and ease.
Visual Memory Techniques
Imagine the apostrophe as a tiny bridge connecting ownership and words. Each placement tells a unique story of connection, making grammar rules come alive through vivid mental imagery.
| Memory Technique | Visual Metaphor | Grammatical Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Singular Possession | Single Bridge | Family’s (One Family) |
| Plural No Possession | Multiple Paths | Families (Multiple Families) |
| Plural Possession | Connecting Bridges | Families’ (Multiple Families Owning) |
| Ownership Connection | Linking Concept | Apostrophe as Relationship Marker |
| Spatial Understanding | Mental Mapping | Grammatical Positioning |
| Emotional Association | Personal Narrative | Linguistic Ownership |
| Contextual Visualization | Scenario Imagination | Practical Application |
| Linguistic Mapping | Cognitive Network | Grammatical Relationships |
| Dynamic Interpretation | Flexible Thinking | Adaptive Language Use |
| Conceptual Bridging | Ownership Visualization | Semantic Connections |
Sound-Based Memorization
Develop a rhythmic mental chant to distinguish between these forms:
- “One Family’s Way” (Emphasize singular possession)
- “Many Families” (Simple plural)
- “Many Families’ Shared Space” (Plural possession)
Mental Mapping Strategies
The Ownership Ladder Technique
Visualize an imaginary ladder where each step represents a different grammatical state:
- Bottom Step: Just “Families” (No ownership)
- Middle Step: “Family’s” (Single family’s ownership)
- Top Step: “Families'” (Multiple families’ shared ownership)
Context Clue Detective Method
Transform grammatical learning into a detective game. Ask yourself these investigative questions:
- How many families are involved?
- Are they owning something?
- What exactly is being possessed?
| Detective Question | Grammatical Clue | Correct Form |
|---|---|---|
| Single Family? | Ownership by one unit | Family’s |
| Multiple Families? | No specific ownership | Families |
| Multiple Families Owning? | Shared possession | Families’ |
| Describing a Group | General reference | Families |
| Specific Family Trait | Individual characteristic | Family’s |
| Collective Action | Group-level ownership | Families’ |
| Personal Connection | Singular family narrative | Family’s |
| Community Perspective | Broader family context | Families |
| Legal Attribution | Ownership documentation | Family’s/Families’ |
| Emotional Dimension | Relational description | Family’s |
Technology-Inspired Memorization
The Autocorrect Mental Model
Think of your brain like a sophisticated language processing system. Train your internal “autocorrect” to recognize these patterns instantly:
- Single Family Ownership = Instant “Family’s” Flag
- Multiple Families = “Families” Neutral State
- Multiple Families Owning = “Families'” Collaborative Flag
Practical Training Exercises
Rapid Recognition Game
Create quick mental scenarios:
- Scenario 1: A birthday invitation from the Johnson family
- Scenario 2: Multiple neighborhood families planning an event
- Scenario 3: Discussing various families’ community contributions
Psychological Anchoring
Grammatical mastery isn’t about memorization—it’s about creating linguistic muscle memory. The more you practice, the more these patterns become second nature.
Neurological Learning Hack
Engage multiple senses when practicing:
- Read the forms aloud
- Write example sentences
- Visualize the ownership scenarios
- Speak the variations with confidence
Technology and Learning
Modern language learning platforms and grammar apps can provide interactive exercises to reinforce these concepts. Consider utilizing digital tools that offer real-time feedback and contextual learning.
Conclusion: Embracing Linguistic Complexity
Writing skills are developed through patient exploration and thoughtful practice. Each apostrophe, each possessive form, tells a story—not just of ownership, but of connection, identity, and shared human experience.
Master the nuance, and you master communication.

Emma Carter is an experienced blogger at Pro English Tips. She loves helping people improve their English skills, especially through synonyms and creative language use. With a friendly writing style, Emma makes learning fun and easy for everyone. In her spare time, she enjoys reading and exploring new words, always looking for ways to inspire her readers on their journey to better communication.